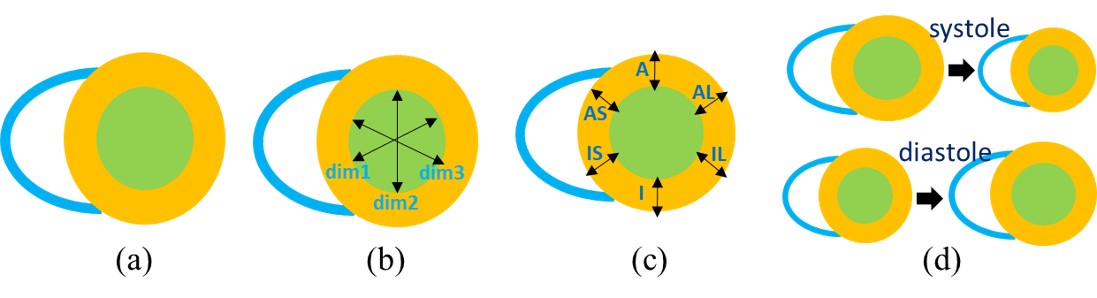
-
Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) are used to assess the performance of the algorithms for estimation of areas, dimensions and regional wall thicknesses. For the 30 subjects in the test dataset, there are a total of 600 images. For any LV indices in {A1, A2, D1~D3, RWT1~RWT6}, the MAE and PCC can be computed as:
where , is the groud truth value and is the estimated value, and are their mean values. -
Error Rate (ER) is used to assess the performance of the algorithms for cardiac phase identification. It can be computed as:
where is the indication function, and are the ground truth value and the estimated value of cardiac phase, respectively.
Ranking
MAE and ER are used for the final ranking of all participants.
- Initialization:
- 1. For each participant, compute for and .
- 2. Compute the mean MAE values for areas, dimensions, and regional wall thicknesses, and obtain , , .
- 3. Build four ranking lists (, , , ) of all participants according to , , and in ascending order, respectively. Statistical test is conducted for areas, dimensions, and regional wall thicknesses to test the significance of difference between two participants. If no significance exists, the two participants will have the same rank in the list.
- 4. The final ranking list is computed by sorting the summation of the four ranking lists above in ascending order.